Once you have downloaded the .pdf or .doc file
and you are ready to do the assignment, you must start the program
by clicking on 'Run Program.' Before you run the program, be sure
you have gone through the CMU Mini-FEA Tutorial. |
Choose Full Assignment (pdf):
|
|
Brief Description of Assignments:
|
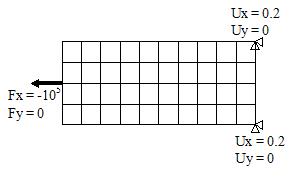
1.1.1
(i) Apply force and displacement boundary conditions on nodes;
(ii) interpret the computed values of displacements Ux and Uy
in terms of the motion shown on the deformed mesh; and (iii)
extract the forces at supports from FEA and show that, together
with any applied forces, the forces keep the body in equilibrium.
|
| 
|
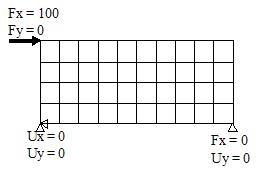
|
|
|
2.1.1
(i) Conduct FEA for bar in axial compression, with force at
one end applied in two ways (concentrated and distributed);
(ii) compare stresses at two points with P/A illustrating St.
Venant’s principle; (iii) compare changes in both axial
and transverse length (based on FEA displacements) with changes
in lengths inferred from simple axial loading theory.
|
|
|
|
|
2.1.2
(i) Apply force and displacement boundary conditions on nodes;
(ii) interpret the computed values of displacements Ux and Uy
in terms of the motion shown on the deformed mesh; and (iii)
extract the forces at supports from FEA and show that, together
with any applied forces, the forces keep the body in equilibrium.
|
|
|
|
|
3.1.1
(i) Conduct FEA for single block with displacements on top and
bottom corresponding to a simple shear; (ii) compare FEA shear
stress at two points in block and total force on top and bottom
sets of nodes with predictions from simple shear).
|
|
|
|
|
3.1.2
(i) Model shearing of two blocks sandwiched between three rigid
plates by conducting FEA for single block with distinct shearing
displacements on top, bottom, and horizontal center line; (ii)
compare FEA shear stress at various points and total force on
line of nodes at top, bottom, and centerline with simple shear
predictions of sandwiched blocks.
|
|
|
|
|
4.1.1
(i) Conduct FEA for long slender bar with displacements fixed
at one end (cantilevered), and equal and opposite forces at
other end (moment); (ii) compare FEA normal stress at various
points in one cross-section with bending theory; (iii) find
deflection, slope (finite difference of displacement at neighboring
nodes), and curvature (finite difference of slope at neighboring
nodes); (iv) compare curvature with M/EI.
|
|
|
|
|
4.1.2
(i) Conduct FEA for long slender bar with equal couples at two
ends, and balancing couple in center; (ii) compare FEA normal
stress at various points in one cross-section with bending theory;
(iii) find deflection, slope (finite difference of displacement
at neighboring nodes), and curvature (finite difference of slope
at neighboring nodes) and compare with M/EI.
|
|
|
|
|
4.1.3
(i) Student is given the deformed mesh, and partial information
on loading: the bar is fixed at one end, has three applied couples
(known magnitudes, unknown locations and senses), and has a
specified maximum bending stress. By studying the deformed mesh,
the student can determine the direction of the curvatures, and
hence, the location and senses of the couples, and compare FEA
normal stresses with predictions of beam theory.
|
|
|
|
|
|